Ginkgo trees are unique, almost immortal plants
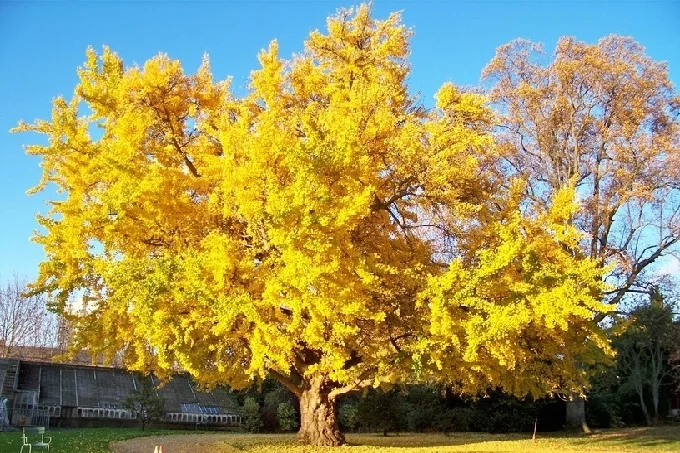

In contrast to oak trees, which may live for hundreds of years and display the effects of time on their appearance, Ginkgo Biloba trees never reveal their age in any manner. And even experts, who have researched this one-of-a-kind plant in great detail guarantee that at the age of 3,000 years, Ginkgo will look and feel as youthful and lovely as it does at the age of a few decades. This is a remarkable fact that scientists have discovered. What makes this plant so special, and how can it be replicated?
Although it has the appearance of a typical deciduous tree, the ginkgo tree is not linked to chestnuts or birches in any way.
In point of fact, it is an old holosemous plant, which, in terms of its evolutionary development, more closely resembles cycad palms or conifers than it does other types of trees and plants. It is unlike the plants of today, which have seeds that are encased in a protective sheath since their seeds do not have this coverage. Paleobotanists have determined that plants belonging to the genus Ginkgo date back to the Triassic period and flourished throughout the Mesozoic, when there were several dozen species of Ginkgo on the planet. Paleobotanists have also determined that fossils have been found that support this hypothesis.
This rare and ancient genus only has one species left on Earth, and that species is the Ginkgo biloba tree. The modern natural habitat of this species is only found in eastern China, but it is cultivated as an ornamental plant in Japan, Korea, and many other countries around the world where the climatic conditions meet certain requirements. The modern natural habitat of this species is only found in eastern China.
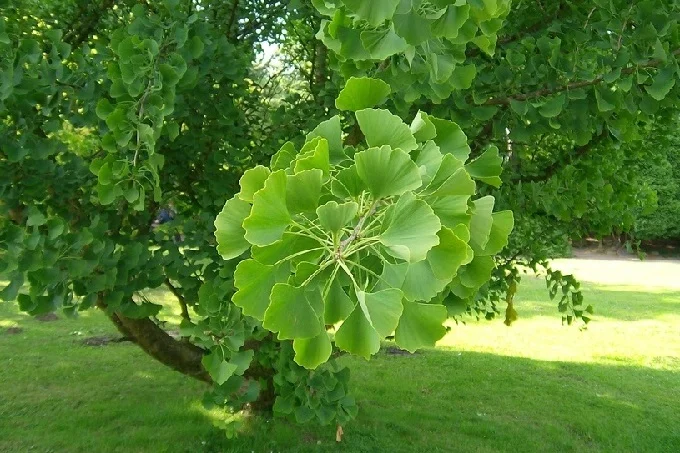

In China, the plant has been included in a wide variety of medicinal preparations for a very long time. Ginkgo may also be found in a variety of dietary supplements, despite the fact that conventional medical practice views the plant’s qualities in a highly equivocal light and that some researchers are skeptical about the plant’s curative potential.
First and foremost, the extraordinary lifespan of the tree continues to pique the curiosity of botanists. Ginkgo trees that are allowed to flourish in their natural environments or in close proximity to monasteries tend to reach an age of about 1,000 years on average, despite the fact that they have the potential to live for up to 3,000 years.
The ages of the Ginkgo trees themselves varied from three to six hundred sixty-seven years, thus the researchers matched tissue samples with the trees themselves. It was discovered that elder trees, in addition to their younger counterparts, had a high level of resistance to infections, which in turn makes them resistant to environmental stresses.
In addition, researchers have discovered that elderly trees have a fast rate of wood development, that their photosynthesis is complete, and that the quality of the seeds that they generate is comparable to that of the progeny of young plants. Despite this, there were still variances discovered.
For instance, aged trees are distinguished by a lower level of growth hormone concentration, and the cambium cells that compose their bark and wood no longer divide as vigorously as they once did. Despite these changes, elderly trees nevertheless show signs of development. In a plant that is more than 500 years old but seems to be no older than a 10-year-old tree in any other way, the markers of age that have been discovered are such insignificant details.
The results, according to the scientists’ interpretation, are only the tip of the iceberg. Continued research into the Ginkgo tree is required if one wants to comprehend the processes that govern the functioning of the plant and, more crucially, to learn how it maintains its youthful appearance over the course of thousands of years.
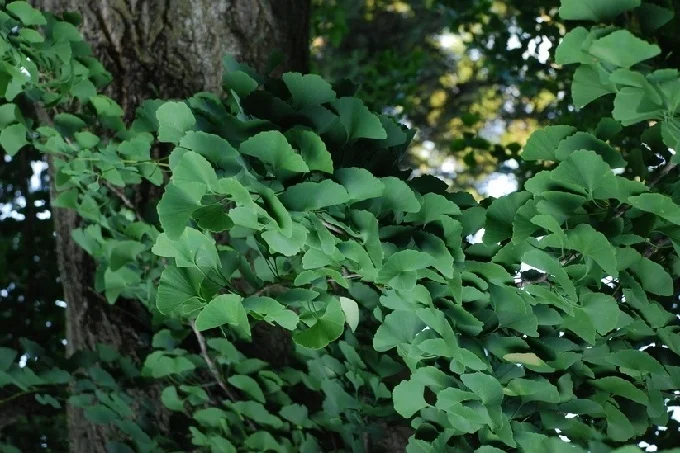

The majority of trees that perish in today’s world do so as a result of natural disasters such as hurricanes or fires; nevertheless, they practically never perish as a result of the processes connected with the maturation of a unique organism. Not only does this tree have an astonishingly long life on the level of the individual, but it also astounds with its vitality on the level of the species as a whole. This is a remarkable achievement. After all, the earliest known ginkgo trees date back to the time when dinosaurs roamed the Earth.
However, it is well knowledge that the huge reptiles fell extinct a long time ago as a result of a natural calamity that occurred on a worldwide scale. However, the Ginkgo tree is still growing in China, giving researchers the rare opportunity to investigate a living relic.