What happens to your body if you don’t get enough sunlight

Regarding sunlight, every person has their own unique point of view. Others believe it encourages the development of various skin diseases, including cancer. In contrast, others believe that it is an extremely beneficial thing that helps to keep one’s immunity and mood at a high level. The truth lies in the middle, and individuals on both sides of the argument are correct.
Sun deficiency is just as dangerous as overexposure to the sun, and if you don’t spend enough time outside in the sunlight, it can seriously impact your health. Sun exposure can be measured in hours, not minutes. The following is a list of the effects that a lack of sunlight has on the body.
1. Vitamin D deficiency occurs
The sun’s rays set off a chain reaction in the skin’s epidermis, which produces vitamin D3 from provitamin D3. After that, it goes into the bloodstream and is carried to the liver, where it is absorbed in the intestines before continuing its journey. Although it is possible to obtain vitamin D from various foods, including beef liver, fatty fish, dairy products, egg yolks, and egg yolks, this is the most suitable and efficient method for increasing vitamin D levels. However, the amount of vitamin D that can be obtained from food is insufficient to fulfil the body’s requirements.
If you don’t get enough sun, you’ll develop a vitamin D deficiency, resulting in the symptoms outlined in the following paragraphs. By the way, vitamin D production is already reduced by sixty percent simply by being in the shade or outside when it is cloudy. Ultraviolet light is required to kickstart the synthesis. Still, it does not penetrate glass or clothing in any way.
2. Sleep and wakefulness cycles are disrupted

The cycles of sleep and wakefulness, also known as circadian rhythms, are innate to us due to our genetic make-up. They are susceptible to being disrupted by various factors, including hormonal disorders and mundane daily routines. The amount of light in the environment significantly impacts this cycle. Because the body stops understanding the difference between, for example, day and dusk, circadian rhythms begin to malfunction without regular exposure to the sun. This is especially true if you are constantly either in a dark environment or under artificial light, which causes the body to stop understanding the difference between day and dusk.
As a consequence of this, there is a possibility of either persistent sleepiness brought on by the continuous production of melatonin or insomnia. Therefore, before you run out to buy energy drinks or sleeping pills, try to change your daily routine and spend more time outside. This will help you feel more refreshed.
3. Hair Loss
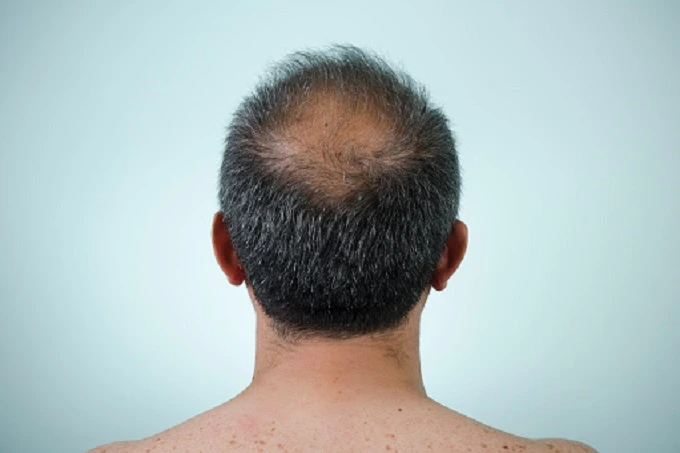
People who spend most of their time sitting inside and rarely venture into the sun are more likely to experience premature balding, as you may have noticed. This is because of a deficiency in vitamin D, which encourages the growth of healthy hair to replace the hair loss due to hair loss. If the hair isn’t getting enough nutrients, it will start to thin out and eventually fall out if the condition persists. Another symptom of a deficiency in vitamin D is increased perspiration of the scalp, which occurs for the same reason.
4. Healing takes a significantly longer amount of time
The exposure of wounds to sunlight has been shown to hasten the healing process. And it’s not just vitamin D and other micronutrients; ultraviolet light itself acts as a disinfectant, destroying a wide variety of infectious agents in addition to the vitamin D and other micronutrients. Because sunlight kills harmful microorganisms, there is less of a chance that inflammation will occur, resulting in a faster recovery time for wounds.
5. Stress and depression

Vitamin D has various effects, one of which is on an individual’s mental health. Studies have shown that the lower your vitamin D levels are, the greater the likelihood you will experience prolonged stress or even depression.
As a side note, this is also why people report feeling less energized during the fall and spring seasons when there is less sunlight.
6. There is an increased likelihood of developing cancer
It is a common belief that spending too much time in the sun can increase the likelihood of developing skin cancer. This is correct, and if you are going to be going outside on a day when the sun is shining brightly, you should apply sunscreen to any areas of your skin that will be exposed.
However, research has shown that exposure to sunlight and the vitamins it produces, such as vitamin D, can help prevent or slow the growth of cancer cells. This is supported by other studies which show that people living in southern latitudes, where the number of sunny days significantly outnumbers the number of cloudy days, have a lower risk of developing certain types of cancer.
7. The heart starts to malfunction

It’s not just a lack of vitamin D; it’s also a lack of other components that sunlight produces, such as the happy hormone. The stress that is brought on by a deficiency in beneficial minerals causes a deterioration of the cardiovascular system, which is also brought on by the impaired absorption of calcium. As a direct consequence of this, high blood pressure, thickened arteries, and various other health issues may develop.
8. Bones and joints lose strength, and muscles become weaker
Calcium is produced and absorbed in the body in a manner that is intricately connected to the effects of sunlight. If not enough, there will be a calcium deficiency, experienced most acutely in the bone and joint tissue. Additionally, it affects the muscles. The lack of sunlight causes the bones to become more fragile and soft, while inflammation causes the joints and muscles to become more brittle and rigid.
In the morning, you might wake up with soreness and stiffness in your muscles and throbbing pain in your bones and joints. You are aware of a decline in your physical strength caused by the fact that your muscles are not working to the best of their abilities.
9. The immune system is weakened

You may notice that you get sick more frequently if you don’t get enough sun. This is not only because your body does not produce an adequate amount of vitamin D but also because your immune system is not being adequately “attacked” by UV light, which would otherwise help it become more disease resistant.
Your metabolism will slow down when there is insufficient exposure to sunlight. These factors lower the body’s resistance when taken together, making it simpler for pathogens like bacteria and viruses to circumvent the body’s inherent defenses.




